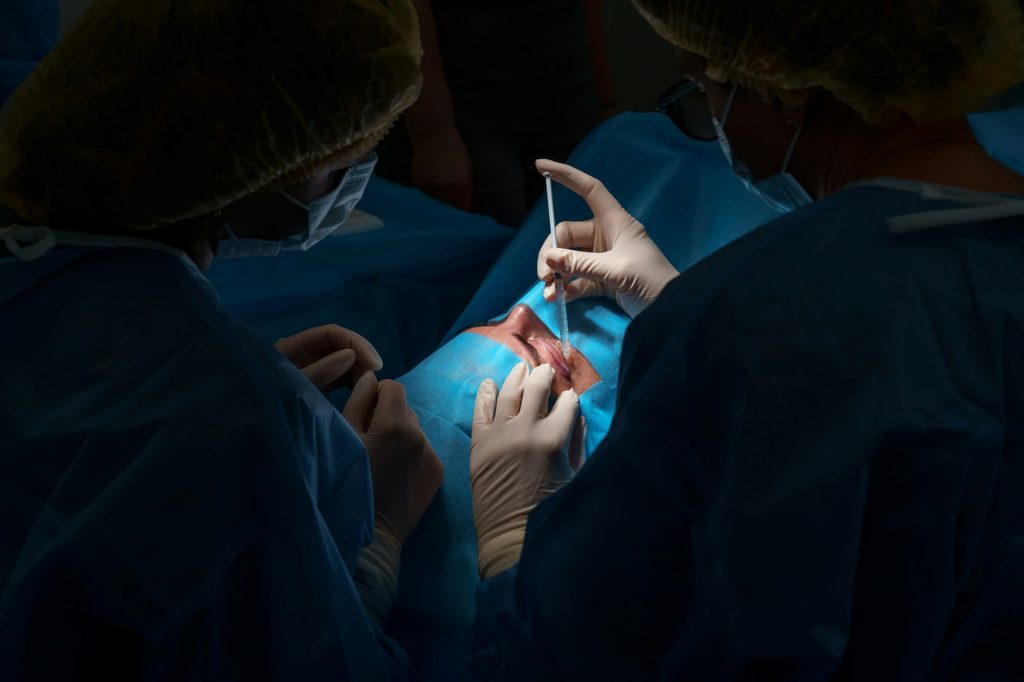
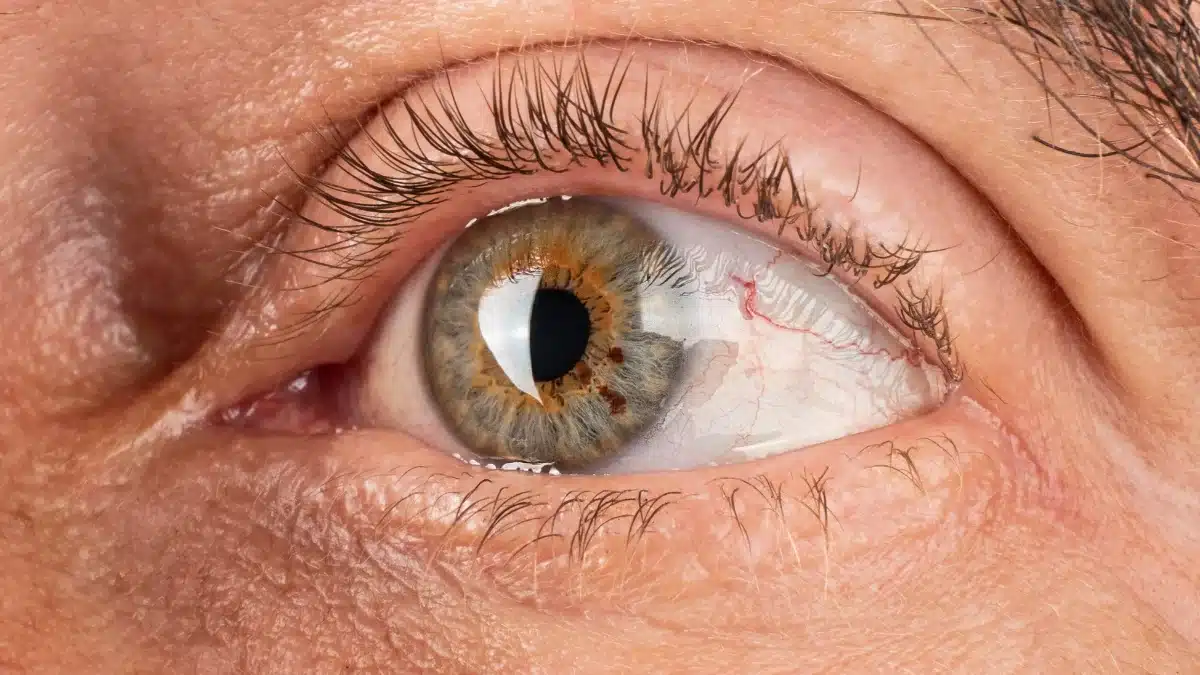
Routinely performed procedures
- Diagnosis and Evaluation: The ophthalmologist examines the cornea for damage, infections, or diseases.
- Treatment Options: Depending on the condition, treatments may include medications, corneal transplantation, or laser surgery.
- Recovery and Monitoring: Post-treatment care includes follow-up appointments to monitor corneal healing and vision recovery.