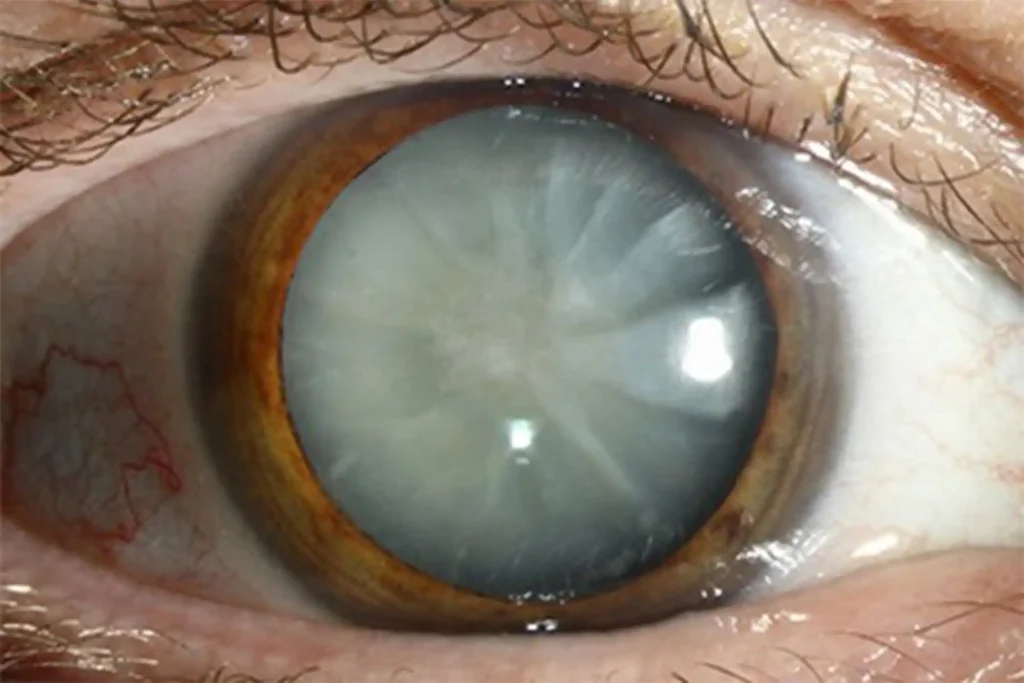
Routinely performed procedures
Phacoemulsification (Phaco Surgery): The most common procedure, where a small incision allows an ultrasound device to break up the cloudy lens. The pieces are removed, and an artificial lens (IOL) is implanted. This quick procedure has a short recovery time.
Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE): For advanced cataracts, ECCE requires a larger incision to remove the lens in one piece, then inserts an IOL. Recovery is longer, but it’s effective for dense cataracts.
Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Surgery: This advanced laser technique makes precise incisions and softens the cataract for removal, yielding excellent outcomes.
Posterior Capsule Opacification (PCO) Treatment: A YAG laser capsulotomy treats post-surgery cloudiness, restoring vision quickly and painlessly.